eDocs Home > BEA AquaLogic Data Services Platform 3.0 Documentation > Data Services Developer's Guide
A Web service is a self-contained, platform-independent unit of business logic that is accessible through application adaptors, as well as standards-based Internet protocols such as HTTP or SOAP.
Web services greatly facilitate application-to-application communication. As such they are increasingly central to enterprise data resources. A familiar example of an externalized Web service is a frequent-update weather portlet or stock quotes portlet that can easily be integrated into a Web application.
Similarly, a Web service can be effectively used to track a drop shipment order from a seller to a manufacturer.
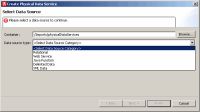
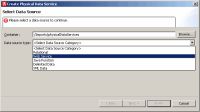
Physical data services are created using a wizard.
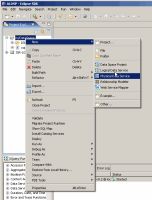
To start the physical data service creation wizard:
- Right-click on your dataspace project or any folder in your project.
- Choose New > Physical Data Service
Once you select web service as your data source, you will be given the option of selecting a URI or WSDL file.
There are several ways to access a specific web service:
- From a Web Service Description Language (WSDL) file located in your current ALDSP project.
- From a WSDL accessible via a URL.
- Through a local proxy service such as is used for AquaLogic Service Bus.

You can test the ability to create a physical data service based on a web service using the following WSDL (available as of this writing): http://www.whitemesa.net/wsdl/r2/base.wsdl
To access web services through AquaLogic Service Bus you need to:
- Provide access and credential information to AquaLogic Service Bus.
- Select a local proxy (if there is more than one).
AquaLogic Service Bus access requires providing the following:
- Server name
- Port number
- User name
- Password
This information should be available from your AquaLogic Service Bus administrator.
Once the required information is provide, the WSDL will become available using the name of the selected proxy service.
- Enter a Web service URL, local WSDL, or ALSB proxy.
- Click Next.
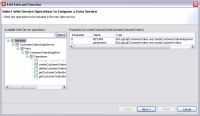
From the list of available webservice operations grouped by serviceName and portname, choose the operation that you want to turn into data service operation.
| During the import process you will be choosing the operations you want to import, setting names and other characteristics. These choices will determine whether a Library or Entity data service will be created. Thus a familiarity with the operations of your Web service is needed. |
You can add operations to an existing physical data service based a web service by adding an external function from the same WSDL.
| Add an External Function to an Existing Physical Data Service |
- Select the operations you want to turn into data services or library data service functions.
- Click Next.
The following table describes available options for each operation you have selected to import.
| Characteristic |
Options |
Comment |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation name |
adjust as needed |
You can change the nominated name to any legal XML name using the built-in line editor. |
||
| Public |
Boolean |
By default Web service-derived operations are protected. A checkbox allows you to mark any function or procedure as public. (Once in a data service, operations can be marked private as needed.) |
||
| Kind |
|
Operations determined to return void are automatically marked as library procedures. You can change the nominated function type. wizard attempts to correctly set the function type dur being imported.
|
||
| is Primary |
Boolean |
Not applicable for web service operations. |
||
| Root Element |
Root element of the operation |
For complex data types the topmost element is listed. In case of RPC-style web services the top-most generated element is listed. |
||
| Target Namespace | imported value | This represents the target namespace of the generated data service. |
You can change the name of your data service to any legal name that does not conflict with another name in the current data space.
In addition, if there already is a data service in your project based on the same WSDL an option to add the new operation to the existing data service appears.
| When importing a web service operation that itself has one or more dependent (or referenced) schemas, the wizard creates second-level schemas according to internal naming conventions. If several operations reference the same secondary schemas, the generated name for the secondary schema may change if you re-import or synchronize with the Web service. |
As of this writing the following sample URIs can be used for experimentation with importing WSDLs as data services:
This section contains implementation notes.
In case of RPC-style web services, results are return as qualified or unqualified based on the setting of the schema attribute:
elementFormDefault
In the general case of web services, elementFormDefault can be overridden by setting the form attribute for any child element. However, such individual settings are ignored for RPC-style web services since only the global setting (qualified or unqualified) is taken into account.
For example:
<s:schema elementFormDefault="qualified" targetNamespace="http://temp.openuri.org/SampleApp/CustomerOrder.xsd" xmlns:s0="http://temp.openuri.org/SampleApp/CustomerOrder.xsd" xmlns:s="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <s:complexType name="ORDER"> <s:sequence> <s:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" form="unqualified" name="ORDER_ID" type="s:string"/> <s:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" form="unqualified" name="CUSTOMER_ID" type="s:string"/> </s:sequence> </s:complexType> </s:schema>
In the above code the global element is qualified but a child element (ORDER_ID) is unqualified.
In the standard case, the special setting of "unqualified" for ORDER_ID will be honored. In the case of RPC-style web services, however, the runtime will generate "qualified" attributes for all the elements, including ORDER_ID.
| RPC-style web services such as those generated by ADO.NET may contain child elements with "form" attributes which do not match the schema's elementFormDefault declaration. In order for such web services to be turned into executable data service operations, make sure that all form element attributes and the elementFormDefault attribute are in agreement (either "qualified" or "unqualified"). |
Multi-dimensional arrays in RPC mode are not supported.
How To Create SOAP Handlers for Imported WSDLs
Contact BEA | Feedback | Privacy | (c) 2008 BEA Systems